- Testing
- Morphology Observation
- Microstructure Analysis
- Surface Element Analysis
- Surface Foreign Body
- Component Analysis
- Mechanical property test
- Thermal Analysis
- Welding Qualification
- CT Scan
- Nondestructive testing
- Cross Section Analysis
- Coating Thickness
- Flame Retardant Test
- Abration Test
- Coating quality inspection
X-ray Diffraction(XRD)
1.X-ray Diffraction(XRD)
X-ray diffraction (XRD) technology is an important research tool for materials. The material composition and structure or form of atoms and molecules of materials can be obtained by analyzing its diffraction pattern.XRD is the main method to study phase and crystal structure of materials. When the material (crystalline or amorphous) is irradiated by X-ray, the different diffraction pattern can be generated, and the material composition, crystal type, molecular bond, molecular configuration and conformation determine the unique diffraction pattern of materials. XRD has the advantage of no damage to the samples, non-pollution, efficiency, high accuracy and getting more information about the integrity of crystals. Thus, the XRD, one of modern scientific analysis methods on material structure and composition, has gradually widely been used in many research fields and productions.
2.Key Application
(1)When a crystal material includes different ingredients and the proportion need to be distinguished, the XRD can be used to identify the ratio of the crystalline phase.
(2)Many properties of materials are determined by the degree of crystallinity. And the XRD can be used to identify the degree of crystallinity of materials.
(3)Development of new materials needs to fully understand its lattice parameters. The XRD can quickly test out the lattice parameters, and provide performance indicators for the verification of new materials development and application.
(4)Products appear the fracture and deformation failure phenomena in the process of use, which may be affected by the micro stress. And the XRD can quickly measure microscopic stress of materials.
(5)Due to the small particles, nanomterials is easy to form pellets. The conventional particle size analysis equipment will often give wrong information. The XRD can calculate the average particle size of nanoparticles by line width method (Scherrer method).
3.Attention
(1)The solid surface of the sample should be more than 10 × 10mm, the thickness of sample is 5μm or above, the surface must be flat, and sample can be stuck together.
(2)For flake, cylindrical sample, there is severe preferred orientation. And it will appear diffraction intensity abnormality, so the test direction needs to be provided.
(3)For the measurement of microscopic stress (lattice distortion) and the measurement of residual austenite in metal sample, the metal sample is required to prepare to be a metallographic sample, and do general polishing or electrolytic polishing to eliminate surface strain layer.
(4)Powder samples require grounding into 320 mesh, about 40 micrometers in diameter and weighing more than 5g.
4.Application Example
Sample information: the inspected sample is a white pearl powder, and the inspection applicant requires doing phase identification. The equipment for this study is RigakuD / max2500 X-ray diffraction.
Test parameters: tube voltage: 40KV, tube current: 200μA, Cu target, diffractive width DS = SS = 1 °, RS = 0.3mm, scan speed 2.000 (d • min-1), scan range of 10°~ 80°.
Test spectrum:
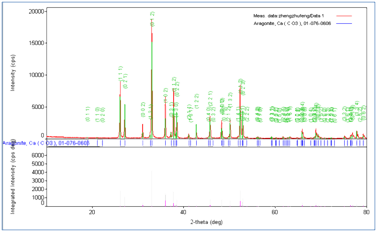
Test results: The main component of the sample is calcium carbonate
- Learn more
- Qualification and honor
- Contact Us
- Contact Us
MTT Shenzhen
Tel: 400-850-4050
Fax: 0755-2782 1672
Email: marketing@mttlab.com
MTT Suzhou
Tel: 400-118-1002
Fax: 0512-6275 9537
Email: marketing@mttlab.com
MTT Shanghai
Tel: 400-118-1002
Email: marketing@mttlab.com
MTT Dongguan
Tel: 400-116-1002
Email:marketing@mttlab.com
